Publications
2023

\(C_2\) generalization of the van Diejen model from the minimal \((D_5,D_5)\) conformal matter
Belal Nazzal and Anton Nedelin
Lett.Math.Phys. 113, 5, 94 (2023)
BIB ABSTRACT
We study superconformal indices of \(4d\) compactifications of the \(6d\) minimal \((D_{N+3},D_{N+3})\) conformal matter theories on a punctured Riemann surface. Introduction of supersymmetric surface defect in these theories is done at the level of the index by the action of the finite difference operators on the corresponding indices. There exist at least three different types of such operators according to three types of punctures with \(A_N\), \(C_N\) and \((A_1)^N\) global symmetries. We mainly concentrate on \(C_2\) case and derive explicit expression for an infinite tower of difference operators generalizing the van Diejen model. We check various properties of these operators originating from the geometry of compactifications. We also provide an expression for the kernel function of both our \(C_2\) operator and previously derived \(A_2\) generalization of van Diejen model. Finally, we also consider compactifications with \(A_N\)-type punctures and derive the full tower of commuting difference operators corresponding to this root system generalizing the result of our previous paper.

Ground state wavefunctions of elliptic relativistic integrable Hamiltonians
Belal Nazzal, Anton Nedelin and Shlomo Razamat
Nucl.Phys.B 996, 116364 (2023)
BIB ABSTRACT
We derive ground state eigenfunctions and eigenvalues of various relativistic elliptic integrable models. The models we discuss appear in computations of superconformal indices of four-dimensional theories obtained by compactifying six-dimensional models on Riemann surfaces. These include, among others, the Ruijsenaars-Schneider model and the van Diejen model. The derivation of the eigenfunctions builds on physical inputs, such as conjectured Lagrangian across dimensions IR dualities and assumptions about the behavior of the indices in the limit of compactifications on surfaces with large genus/number of punctures/flux.
2022
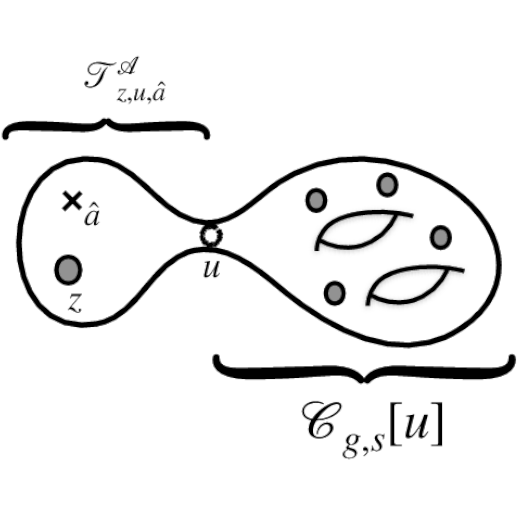
Minimal \((D,D)\) conformal matter and generalizations of the van Diejen model
Belal Nazzal, Anton Nedelin and Shlomo Razamat
SciPost Phys. 12, 4, 140 (2022)
BIB ABSTRACT
We consider supersymmetric surface defects in compactifications of the \(6d\) minimal \((D_{N+3},D_{N+3})\) conformal matter theories on a punctured Riemann surface. For the case of \(N=1\) such defects are introduced into the supersymmetric index computations by an action of the \(BC_1(∼A1∼C1)\) van Diejen model. We (re)derive this fact using three different field theoretic descriptions of the four dimensional models. The three field theoretic descriptions are naturally associated with algebras \(A_{N=1}\), \(C_{N=1}\), and \((A_1)^{N=1}\). The indices of these \(4d\) theories give rise to three different Kernel functions for the \(BC_1\) van Diejen model. We then consider the generalizations with \(N>1\). The operators introducing defects into the index computations are certain \(A_N\), \(C_N\), and \((A_1)^N\) generalizations of the van Diejen model. The three different generalizations are directly related to three different effective gauge theory descriptions one can obtain by compactifying the minimal \((D_{N+3},D_{N+3})\) conformal matter theories on a circle to five dimensions. We explicitly compute the operators for the \(A_N\) case, and derive various properties these operators have to satisfy as a consequence of \(4d\) dualities following from the geometric setup. In some cases we are able to verify these properties which in turn serve as checks of said dualities. As a by-product of our constructions we also discuss a simple Lagrangian description of a theory corresponding to compactification on a sphere with three maximal punctures of the minimal \((D_5,D_5)\) conformal matter and as consequence give explicit Lagrangian constructions of compactifications of this \(6d\) SCFT on arbitrary Riemann surfaces.
2021

Five-dimensional gauge theories on spheres with negative couplings
Joseph Minahan and Anton Nedelin
JHEP 02, 102 (2021)
BIB ABSTRACT
We consider supersymmetric gauge theories on \(S^5\) with a negative Yang-Mills coupling in their large \(N\) limits. Using localization we compute the partition functions and show that the pure \(SU(N)\) gauge theory descends to an \(SU(N/2)_{+N/2} \times SU(N/2)_{−N/2}\times SU(2)\) Chern-Simons gauge theory as the inverse ’t Hooft coupling is taken to negative infinity for \(N\) even. The Yang-Mills coupling of the \(SU(N/2)_{\pm N/2}\) is positive and infinite, while that on the \(SU(2)\) goes to zero. We also show that the odd \(N\) case has somewhat different behavior. We then study the \(SU(N/2)_{N/2}\) pure Chern-Simons theory. While the eigenvalue density is only found numerically, we show that its width equals \(1\) in units of the inverse sphere radius, which allows us to find the leading correction to the free energy when turning on the Yang-Mills term. We then consider \(USp(2N)\) theories with an antisymmetric hypermultiplet and \(N_f\) fundamental hypermultiplets and carry out a similar analysis. Along the way we show that the one-instanton contribution to the partition function remains exponentially suppressed at negative coupling for the \(SU(N)\) theories in the large \(N\) limit.
2020
Black hole entropy function for toric theories via Bethe Ansatz
Assaf Lanir, Anton Nedelin and Orr Sela
JHEP 04, 091 (2020)
BIB ABSTRACT
We evaluate the large-\(N\) behavior of the superconformal indices of toric quiver gauge theories, and use it to find the entropy functions of the dual electrically charged rotating \(AdS_5\) black holes. To this end, we employ the recently proposed Bethe Ansatz method, and find a certain set of solutions to the Bethe Ansatz Equations of toric theories. This, in turn, allows us to compute the large-\(N\) behavior of the index for these theories, including the infinite families \(Y^{pq}\) , \(X^{pq}\) and \(L^{pqr}\) of quiver gauge theories. Our results are in perfect agreement with the predictions made recently using the Cardy-like limit of the superconformal index. We also explore the index structure in the space of chemical potentials and describe the pattern of Stokes lines arising in the conifold theory case.
Supersymmetric Yang-Mills, Spherical Branes, and Precision Holography
N.Bobev, P.Bomans, F.Gautason, J.Minahan, A.Nedelin
JHEP 03, 047 (2020)
BIB ABSTRACT
Using supersymmetric localization we compute the free energy and BPS Wilson loop vacuum expectation values for planar maximally supersymmetric Yang-Mills theory on \(S^d\) in the strong coupling limit for \(2\leq d < 6\). The same calculation can also be performed in supergravity using the recently found spherical brane solutions. We find excellent agreement between the two sets of results. This constitutes a non-trivial precision test of holography in a non-conformal setting. The free energy of maximal SYM on \(S^6\) diverges in the strong coupling limit which might signify the onset of little string theory. We show how this divergence can be regularized both in QFT and in supergravity. We also consider \(d=7\) with a small negative ’t Hooft coupling and show that the free energy and Wilson loop vacuum expectation value agree with the results from supergravity after addressing some subtleties.
2019

\(T[SU(N)]\) duality webs: mirror symmetry, spectral duality and gauge/CFT correspondences
Anton Nedelin, Sara Pasquetti and Yegor Zenkevich
JHEP 02, 176 (2019)
BIB ABSTRACT
We study various duality webs involving the \(3d\) \(FT[SU(N)]\) theory, a close relative of the \(T[SU(N)]\) quiver tail. We first map the partition functions of \(FT[SU(N)]\) and its \(3d\) spectral dual to a pair of spectral dual \(q\)-Toda conformal blocks. Then we show how to obtain the \(FT[SU(N)]\) partition function by Higgsing a \(5d\) linear quiver gauge theory, or equivalently from the refined topological string partition function on a certain toric Calabi-Yau three-fold. \(3d\) spectral duality in this context descends from \(5d\) spectral duality. Finally we discuss the \(2d\) reduction of the \(3d\) spectral dual pair and study the corresponding limits on the \(q\)-Toda side. In particular we obtain a new direct map between the partition function of the \(2d\) \(FT[SU(N)]\) GLSM and an \((N+2)\)-point Toda conformal block.
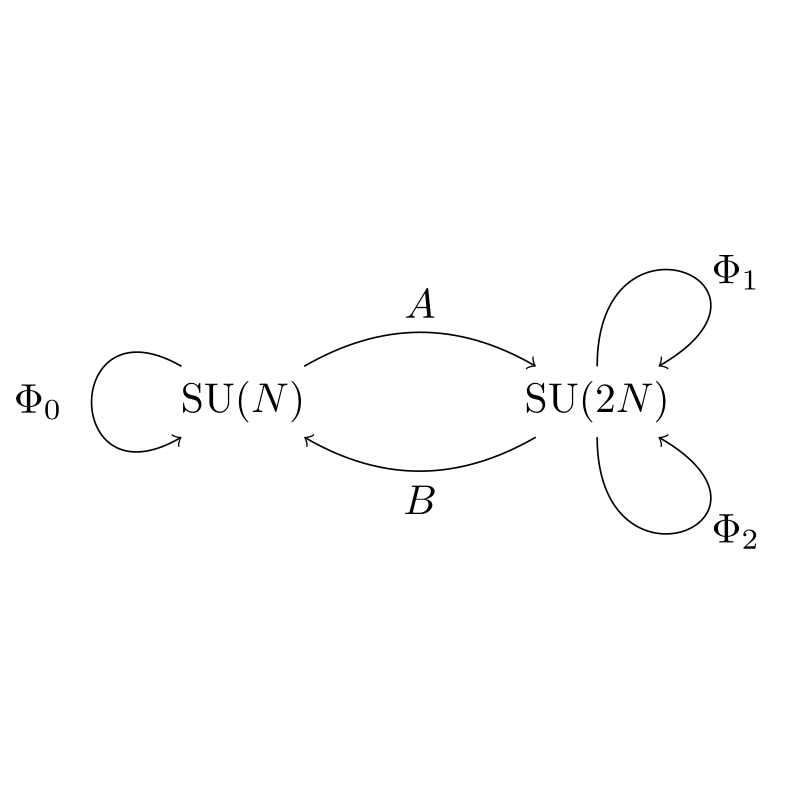
New \(3d\) \(\mathcal{N}=2\) SCFT’s with \(N^{3/2}\) scaling
A.Amariti, M.Fazzi, N.Mekareeya, A.Nedelin
JHEP 12, 111 (2019)
BIB ABSTRACT
We construct several novel examples of \(3d\) \(\mathcal{N} = 2\) models whose free energy scales as \(N^{3/2}\) at large \(N\) . This is the first step towards the identification of field theories with an M-theory dual. Furthermore, we match the volumes extracted from the free energy with the ones computed from the Hilbert series. We perform a similar analysis for the \(4d\) \(\mathcal{N} = 1\) parents of the \(3d\) models, matching the volume extracted from the central charge to that obtained from the Hilbert series. For some of the \(4d\) models, we show the existence of a Sasaki-Einstein metric on the internal space of the candidate type IIB gravity dual.
2017

\(q\)-Virasoro constraints in matrix models
Anton Nedelin and Maxim Zabzine
JHEP 03, 098 (2017)
BIB ABSTRACT
The Virasoro constraints play the important role in the study of matrix models and in understanding of the relation between matrix models and CFTs. Recently the localization calculations in supersymmetric gauge theories produced new families of matrix models and we have very limited knowledge about these matrix models. We concentrate on elliptic generalization of hermitian matrix model which corresponds to calculation of partition function on \(S^3\times S^1\) for vector multiplet. We derive the \(q\)-Virasoro constraints for this matrix model. We also observe some interesting algebraic properties of the \(q\)-Virasoro algebra.

\(q\)-Virasoro modular double and \(3d\) partition functions
Anton Nedelin, Fabrizio Nieri and Maxim Zabzine
Commun.Math.Phys. 353(2017) 3, 1059-1102 (2017)
BIB ABSTRACT
We study partition functions of \(3d\) \(\mathcal{N}=2\) \(U(N)\) gauge theories on compact manifolds which are \(S^1\) fibrations over \(S^2\). We show that the partition functions are free field correlators of vertex operators and screening charges of the \(q\)-Virasoro modular double, which we define. The inclusion of supersymmetric Wilson loops in arbitrary representations allows us to show that the generating functions of Wilson loop vacuum expectation values satisfy two \(SL(2,\mathbb{Z})\)-related commuting sets of \(q\)-Virasoro constraints. We generalize our construction to \(3d\) \(\mathcal{N}=2\) unitary quiver gauge theories and as an example we give the free boson realization of the ABJ(M) model.

The Cardy limit of the topologically twisted index and black strings in \(AdS_5\)
Seyed Morteza Hosseini, Anton Nedelin and Alberto Zaffaroni
JHEP 04, 014 (2017)
BIB ABSTRACT
We evaluate the topologically twisted index of a general four-dimensional \(\mathcal{N}=1\) gauge theory in the “high-temperature” limit. The index is the partition function for \(\mathcal{N}=1\) theories on \(S^2\times T^2\), with a partial topological twist along \(S^2\), in the presence of background magnetic fluxes and fugacities for the global symmetries. We show that the logarithm of the index is proportional to the conformal anomaly coefficient of the two-dimensional \(\mathcal{N}=(0,2)\) SCFTs obtained from the compactification on \(S^2\). We also present a universal formula for extracting the index from the four-dimensional conformal anomaly coefficient and its derivatives. We give examples based on theories whose holographic duals are black strings in type IIB backgrounds \(AdS_5\times SE_5\), where \(SE_5\) five-dimensional Sasaki-Einstein spaces.
2015

Phase transitions in 5D super Yang-Mills theory
Anton Nedelin
JHEP 07, 004 (2015)
BIB ABSTRACT
In this paper we study a phase structure of 5D \(\mathcal{N}=1\) super Yang-Mills theory with massive matter multiplets and \(SU(N)\) gauge group. In particular, we are interested in two cases: theory with \(N_f\) massive hypermultiplets in the fundamental representation and theory with one adjoint massive hypermultiplet. If these theories are considered on \(S^5\) their partition functions can be localized to matrix integrals, which can be approximated by their values at saddle points in the large-\(N\) limit. We solve saddle point equations corresponding to the decompactification limit of both theories. We find that in the case of the fundamental hypermultiplets theory experiences third-order phase transition when coupling is varied. We also show that in the case of one adjoint hypermultiplet theory experiences infinite chain of third-order phase transitions, while interpolating between weak and strong coupling regimes.
2014
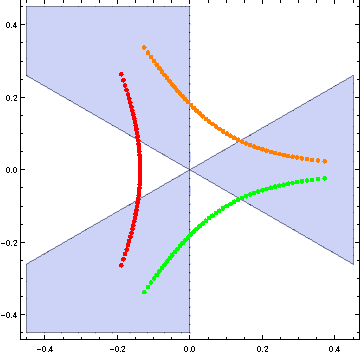
Phases of planar 5-dimensional supersymmetric Chern-Simons theory
Joseph Minahan and Anton Nedelin
JHEP 12, 049 (2014)
BIB ABSTRACT
In this paper we investigate the large-\(N\) behavior of 5-dimensional \(\mathcal{N} = 1\) super Yang-Mills with a level \(k\) Chern-Simons term and an adjoint hypermultiplet. As in three-dimensional Chern-Simons theories, one must choose an integration contour to completely define the theory. Using localization, we reduce the path integral to a matrix model with a cubic action and compute its free energy in various scenarios. In the limit of infinite Yang-Mills coupling and for particular choices of the contours, we find that the free-energy scales as \(N^{5/2}\) for \(U(N)\) gauge groups with large values of the Chern-Simons ’t Hooft coupling, \(\widetilde{\lambda} ≡ N/k\). If we also set the hypermultiplet mass to zero, then this limit is a superconformal fixed point and the \(N^{5/2}\) behavior parallels other fixed points which have known supergravity duals. We also demonstrate that \(SU(N)\) gauge groups cannot have this \(N^{5/2}\) scaling for their free-energy. At finite Yang-Mills coupling we establish the existence of a third order phase transition where the theory crosses over from the Yang-Mills phase to the Chern-Simons phase. The phase transition exists for any value of \(\widetilde{\lambda}\) , although the details differ between small and large values of \(\widetilde{\lambda}\) . For pure Chern-Simons theories we present evidence for a chain of phase transitions as \(\widetilde{\lambda}\) is increased.
2013
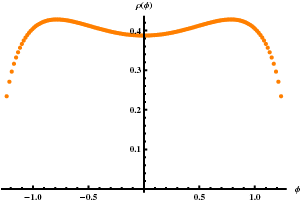
5D super Yang-Mills theory and the correspondence to \(AdS_7/CFT_6\)$
Joseph Minahan, Anton Nedelin and Maxim Zabzine
J.Phys.A 46, 355401 (2013)
BIB ABSTRACT
We study the relation between 5D super Yang–Mills theory and the holographic description of 6D \((2, 0)\) superconformal theory. We start by clarifying some issues related to the localization of SYM with matter on \(S^5\). We concentrate on the case of a single adjoint hypermultiplet with a mass term and argue that the theory has a symmetry enlargement at mass \(M = 1/(2r)\), where \(r\) is the \(S^5\) radius. However, in order to have a well-defined localization locus it is necessary to rotate \(M\) onto the imaginary axis, breaking the enlarged symmetry. Based on our prescription, the imaginary mass values are physical and we show how the localized path integral is consistent with earlier results for 5D SYM in flat space. We then compute the free energy and the expectation value for a circular Wilson loop in the large N limit. The Wilson loop calculation shows a mass dependent constant rescaling between weak and strong coupling. The Wilson loop continued back to to the enlarged symmetry point is consistent with a supergravity computation for an \(M2\) brane using the standard identification of the compactification radius and the 5D coupling. If we continue back to the physical regime and use this value of the mass to determine the compactification radius, then we find agreement between the SYM free energy and the corresponding supergravity calculation. We also verify numerically some of our analytic approximations.
2012
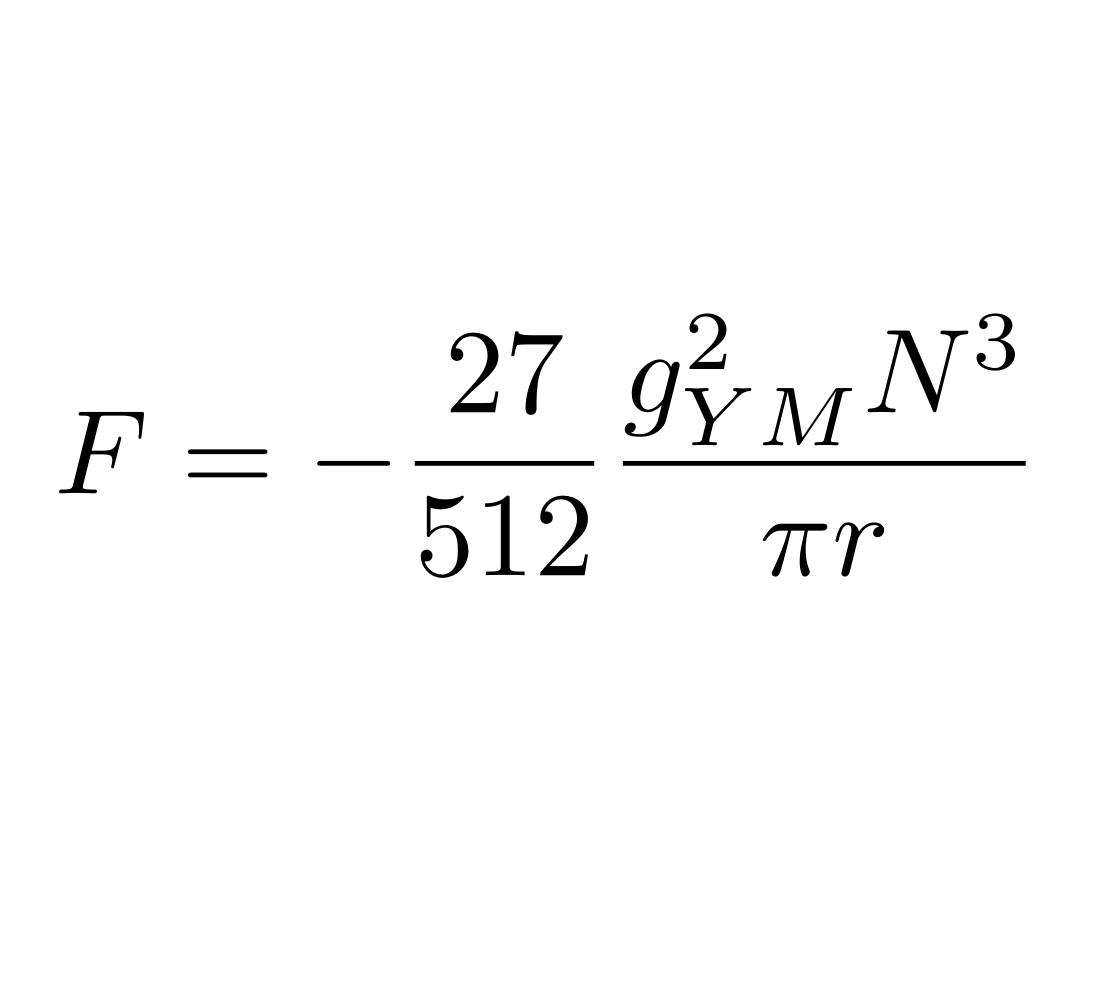
\(N^3\)-behavior from 5D Yang-Mills theory
J.Kallen, J.A.Minahan, A.Nedelin, M.Zabzine
JHEP 10, 184 (2012)
BIB ABSTRACT
In this note we derive \(N^3\)-behavior at large t’ Hooft coupling for the free energy of 5D maximally supersymmetric Yang-Mills theory on \(S^5\). We also consider a \(Z_k\) quiver of this model, as well as a model with \(M\) hypermultiplets in the fundamental representation. We compare the results to the supergravity description and comment on their relation.
2011
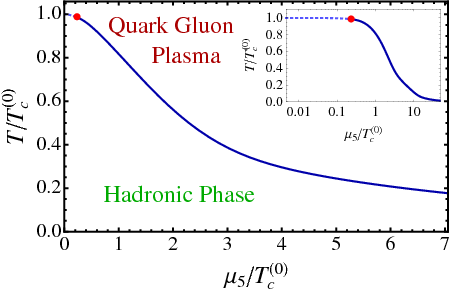
Phase diagram of chirally imbalanced QCD matter
Maxim Chenrodub and Anton Nedelin
Phys. Rev. D 83, 105008 (2011)
BIB ABSTRACT
We compute the QCD phase diagram in the plane of the chiral chemical potential and temperature using the linear sigma model coupled to quarks and to the Polyakov loop. The chiral chemical potential accounts for effects of imbalanced chirality due to QCD sphaleron transitions which may emerge in heavy-ion collisions. We found three effects caused by the chiral chemical potential: the imbalanced chirality (i) tightens the link between deconfinement and chiral phase transitions; (ii) lowers the common critical temperature; (iii) strengthens the order of the phase transition by converting the crossover into the strong first order phase transition passing via the second order end-point. Since the fermionic determinant with the chiral chemical potential has no sign problem, the chirally imbalanced QCD matter can be studied in numerical lattice simulations.
2010
Pipelike current-carrying vortices in two-component condensates
Maxim Chenrodub and Anton Nedelin
Phys. Rev. D 81, 125022 (2010)
BIB ABSTRACT
We study straight vortices with global longitudinal currents in the Bogomol’ny limit of the Abelian Higgs model with two charged scalar fields. The model possesses global SU(2) and local electromagnetic U(1) symmetries spontaneously broken to global U(1) group, and corresponds to a semilocal limit of the standard electroweak model. We show that the contribution of the global SU(2) current to the vortex energy is proportional to the total current squared. Locally, these vortices carry also longitudinal electromagnetic currents, while the total electromagnetic current flowing through a transverse section of the vortex is always zero. The vortices with high winding numbers have, in general, a nested pipelike structure. The magnetic field of the vortex is concentrated at a certain distance from the geometric center of the vortex, thus resembling a ‘‘pipe’’. This magnetic pipe is layered between two electrically charged pipes that carry longitudinal electric currents in opposite directions.